T
Teach Me AnythingTMA
Video History
Page 29 / 43![Find the indicated limit by using the limits
\[
\lim_{(x,y)\to(a,b)} f(x,y) = 5 \quad \text{and} \quad
\lim_{(x,y)\to(a,b)} g(x,y) = -4.
\]
\[
\lim_{(x,y)\to(a,b)} [f(x,y) - g(x,y)]
\]
**Answer:** 9
1.解题 2.讲题 3.使用 MathTex 显示中文](https://manimvideo.explanation.fun/video/cover/578839233902342145.png)
▶
Find the indicated limit by using the limits \[ \lim_{(x,y)\to(a,b)} f(x,y) = 5 \quad \text{and} \quad \lim_{(x,y)\to(a,b)} g(x,y) = -4. \] \[ \lim_{(x,y)\to(a,b)} [f(x,y) - g(x,y)] \] **Answer:** 9 1.解题 2.讲题 3.使用 MathTex 显示中文
![Find the limit (if it exists). (If an answer does not exist, enter DNE.)
\[
\lim_{(x,y)\to(0,0)} \frac{x + y}{x^7 + y}
\]
**Answer:** DNE
1.讲题 2.解题 3.使用 MathTex 显示公式](https://manimvideo.explanation.fun/video/cover/578838266972663809.png)
▶
Find the limit (if it exists). (If an answer does not exist, enter DNE.) \[ \lim_{(x,y)\to(0,0)} \frac{x + y}{x^7 + y} \] **Answer:** DNE 1.讲题 2.解题 3.使用 MathTex 显示公式
▶
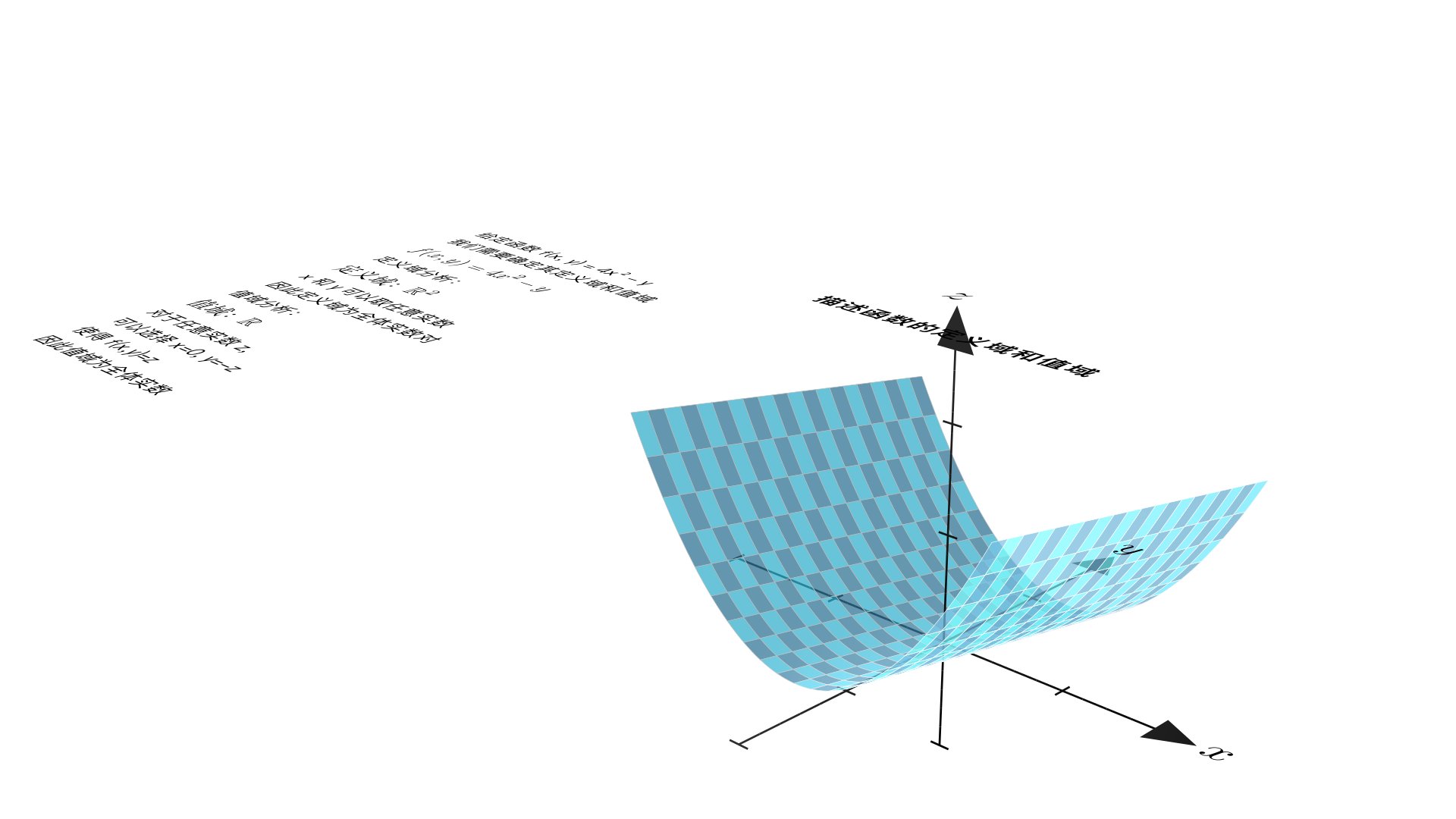
Describe the domain and range of the function. f(x, y) = 4x^2 − y 1.讲题 2.解题 3.使用 MathTex 显示公式
▶
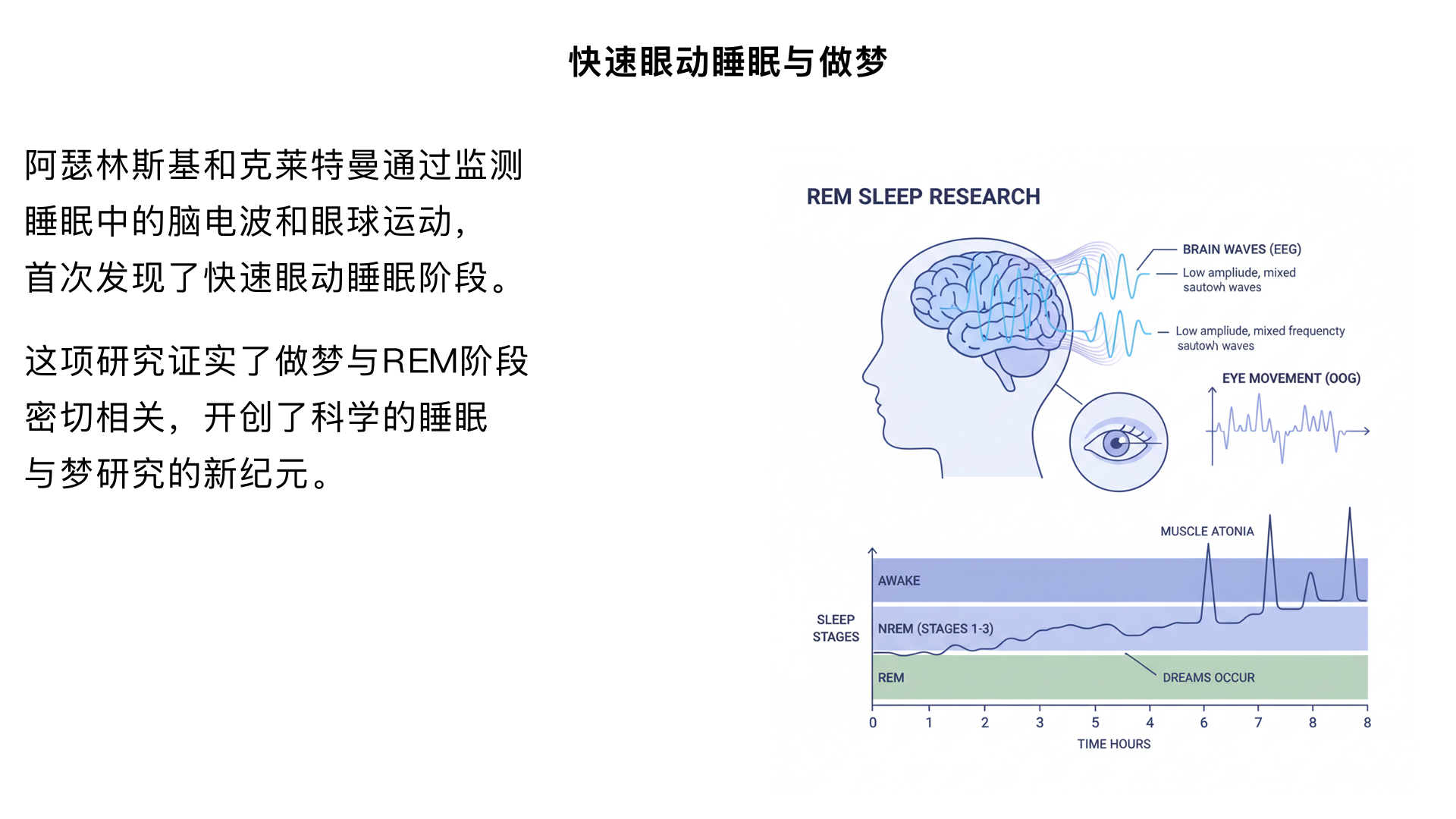
6、睡眠,毫无疑问就会做梦 (阿瑟林斯基和克莱特曼的“快速眼动睡眠”研究) 主要内容:通过监测睡眠中的脑电波和眼球运动,首次发现了快速眼动睡眠阶段,并证实了做梦与此阶段密切相关。这项研究开创了科学的睡眠与梦研究的新纪元。
▶
什么是偏导数
▶
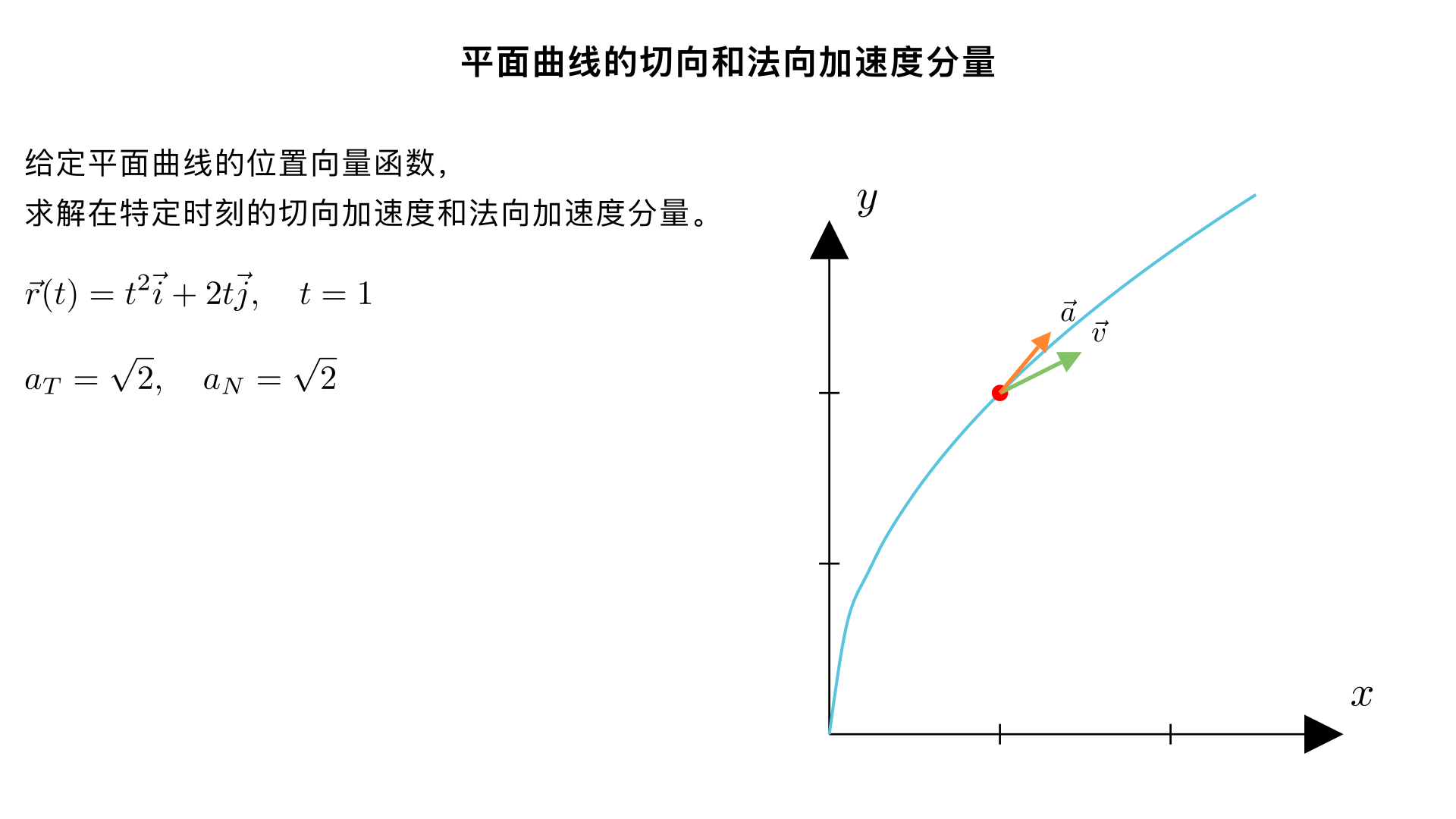
Find the tangential and normal components of acceleration at the given time t for the plane curve **r(t)**. **r(t) = t² i + 2t j, t = 1** \( a_T = \sqrt{2} \) \( a_N = \sqrt{2} \) 1.讲题 2.解题 3.使用 MathTex 显示公式
![**Find the limit (if it exists). (If an answer does not exist, enter DNE.)**
[
\lim_{t \to 0} \left( e^{4t},\mathbf{i} + \frac{\sin(5t)}{5t},\mathbf{j} + e^{-8t},\mathbf{k} \right)
]
**Answer:**
[
\mathbf{i} + \mathbf{j} + \mathbf{k}
]
讲题 解题 使用 Mathtex 显示公式](https://manimvideo.explanation.fun/video/cover/578817939683647489.png)
▶
**Find the limit (if it exists). (If an answer does not exist, enter DNE.)** [ \lim_{t \to 0} \left( e^{4t},\mathbf{i} + \frac{\sin(5t)}{5t},\mathbf{j} + e^{-8t},\mathbf{k} \right) ] **Answer:** [ \mathbf{i} + \mathbf{j} + \mathbf{k} ] 讲题 解题 使用 Mathtex 显示公式
▶
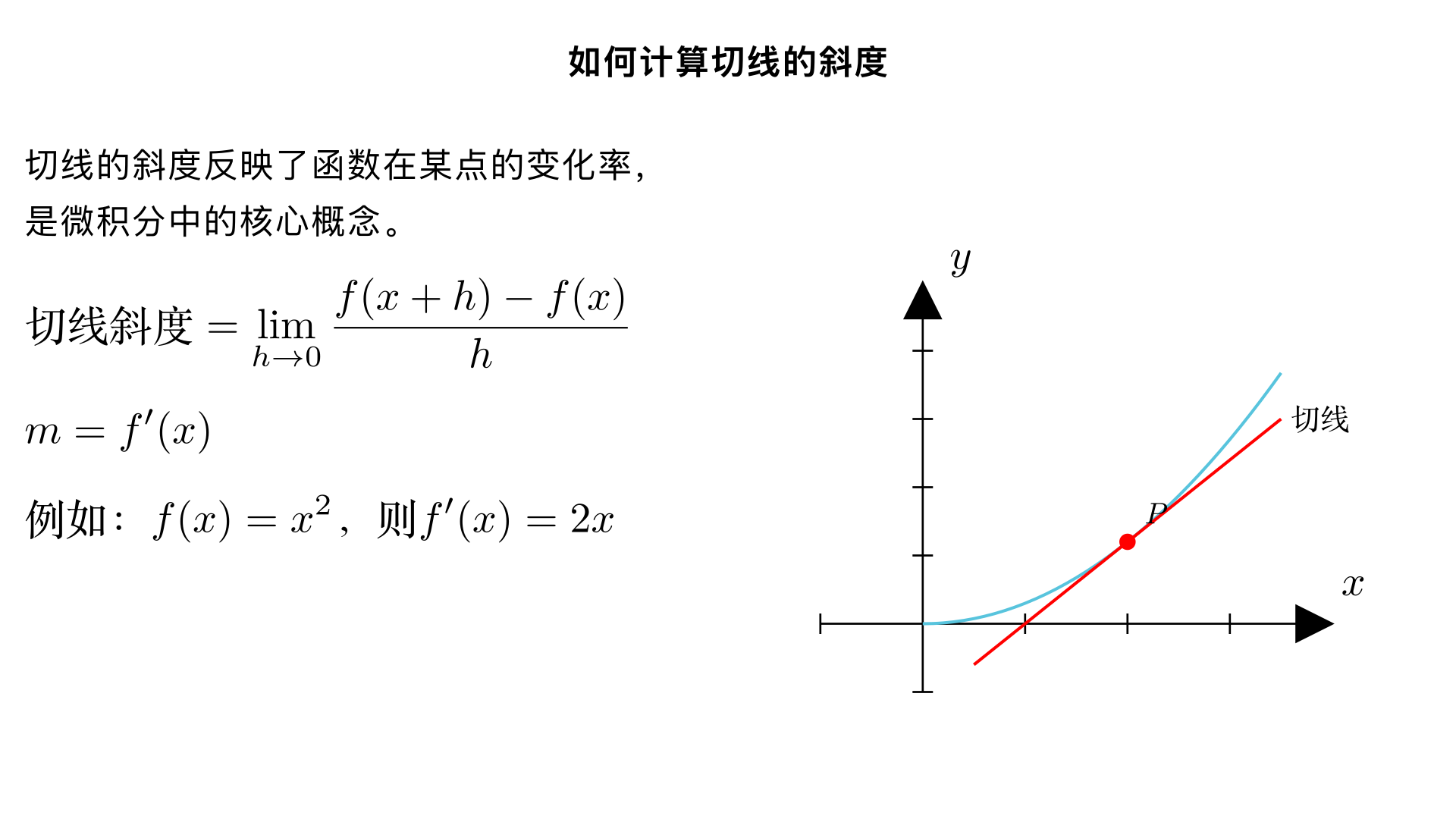
如何计算切线的斜度
![Find the indefinite integral. (Use **c** for the constant of integration.)
\[
\int (2t\,\mathbf{i} + \mathbf{j} + 5\mathbf{k}) \, dt
\]
1.讲题 2.解题](https://manimvideo.explanation.fun/video/cover/578772319945928705.png)
▶
Find the indefinite integral. (Use **c** for the constant of integration.) \[ \int (2t\,\mathbf{i} + \mathbf{j} + 5\mathbf{k}) \, dt \] 1.讲题 2.解题
![## The position vector **r** describes the path of an object moving in the xy-plane.
### **Position Vector**
[
r(t) = t^2 \mathbf{i} + t \mathbf{j}
]
### **Point**
[
(4,, 2)
]
---
### **(a)** Find the velocity vector (v(t)), speed (s(t)), and acceleration vector (a(t)) of the object.
[
v(t) = \langle 2t,\ 1 \rangle
]
[
s(t) = \sqrt{4t^2 + 1}
]
[
a(t) = \langle 2,\ 0 \rangle
]
---
### **(b)** Evaluate the velocity vector and acceleration vector of the object at the given point.
[
v(2) = \langle 4,\ 1 \rangle
]
[
a(2) = \langle 2,\ 0 \rangle
]
1.讲解题目是什意思? 2.讲解解题过程](https://manimvideo.explanation.fun/video/cover/578766165717835777.png)
▶
## The position vector **r** describes the path of an object moving in the xy-plane. ### **Position Vector** [ r(t) = t^2 \mathbf{i} + t \mathbf{j} ] ### **Point** [ (4,, 2) ] --- ### **(a)** Find the velocity vector (v(t)), speed (s(t)), and acceleration vector (a(t)) of the object. [ v(t) = \langle 2t,\ 1 \rangle ] [ s(t) = \sqrt{4t^2 + 1} ] [ a(t) = \langle 2,\ 0 \rangle ] --- ### **(b)** Evaluate the velocity vector and acceleration vector of the object at the given point. [ v(2) = \langle 4,\ 1 \rangle ] [ a(2) = \langle 2,\ 0 \rangle ] 1.讲解题目是什意思? 2.讲解解题过程
![Find the gradient of the function at the given point. \( f(x, y) = 3x + 4y^2 + 1,\quad (1, 3) \) \[ \nabla f(1, 3) = \boxed{\ } \]
解释一下什么是梯度gradient,在现实世界中gradient表示什么?](https://manimvideo.explanation.fun/video/cover/578763141711753217.png)
▶
Find the gradient of the function at the given point. \( f(x, y) = 3x + 4y^2 + 1,\quad (1, 3) \) \[ \nabla f(1, 3) = \boxed{\ } \] 解释一下什么是梯度gradient,在现实世界中gradient表示什么?
![Find the gradient of the function at the given point.
\( f(x, y) = 3x + 4y^2 + 1,\quad (1, 3) \)
\[
\nabla f(1, 3) = \boxed{\ }
\]
注意使用 MathTex 显示公式](https://manimvideo.explanation.fun/video/cover/578760753267503105.png)
▶